Insertion Loss of Enclosures with Lined Slits
Paweł Nieradka
Sound-insulating enclosures are specially designed housings inside which a noise source is placed. The effect of using the sound-insulating enclosure on the source is introducing a significant noise level reduction in the surroundings of a noise source. Often, for technological reasons, the presence of various holes and slits in the walls of the enclosure is required. Unfortunately, any leaks deteriorate the acoustic performance of the housing. Experiments were carried out in the reverberation chamber of KFB Acoustics to check the effect of these leaks on the overall sound-insulating performance of the enclosure (more precisely: insertion loss). The walls of the enclosures were made of MDF boards, while the inside of the enclosures was lined with sound-absorbing material
The tests also included simulations of insertion loss. Simple engineering formulas were used and compared with more advanced Statistical Energy Analysis (SEA) models. Then, the measurement results were compared with simulations – good compliance was obtained for all tested slits and for the entire tested frequency range. The influence of the absorption layer directly above the gaps was also investigated. In this case, a satisfactory agreement was obtained between the simulations and measurements for narrow gaps and in the low frequency range. Figure 1 shows the simulated and measured enclosure insertion loss for various leakage ratios.
Figure 1.
The obtained test results confirmed that simulations using statistical methods provide the best results when the volume of the simulated enclosures is large enough (it is related to the parameter called modal overlap) – as shown in Figure 2, where enclosure E2 was bigger than E1.
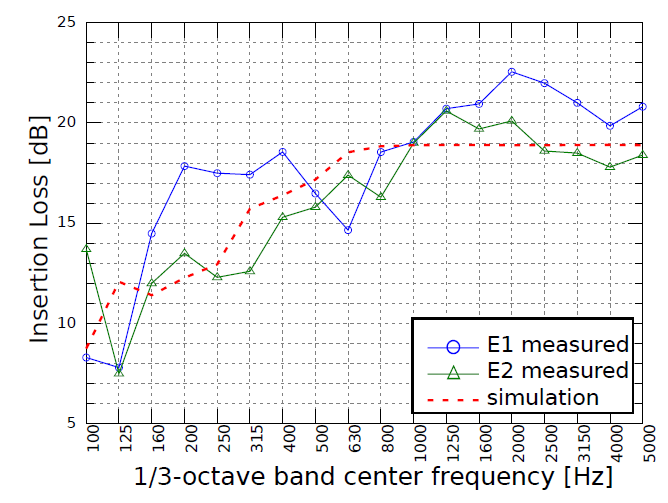
Figure 2.

