Auralization – Acoustic rendering
prof. Monika Rychtarikova
Auralization refers to the process in which a measured or simulated sound field is made audible. Auralization has thus become an attractive tool to communicate efficiently between the acoustic consultancy offices and customers without acoustic background.

BRIEF OVERVIEW
One of the first known attempts to perform an auralization was probably done by Spandök, who used a scale model for this experiment. Anechoically recorded speech and music was first scaled in frequency domain, in the same ratio as the scaled model of the room. This sound was played and recorded in the physical model and afterwards rescaled back to a real scale.
Later on, several researchers have used similar techniques. The use of the digital filters started with more advanced computers and multiple-loudspeaker auralization systems containing from 10 to 50 loudspeaker setups in anechoic rooms. These techniques emerged in the 1960s, in work by Meyer et al (1965), Kleiner (1980), Bech (1990) and others.
Nowadays, the approach for generating auralizations in room acoustics is based on the measurement or simulation of the binaural impulse response between the sound source and receiver, which is later convolved with an anechoic sound wave. Playback can be achieved afterwards via headphones or by a loudspeaker- sound play-back system.
Current auralization techniques use approximations of the room geometry, sound source and receiver properties. Nevertheless, it is important to model the sound source in acoustic models and to record the anechoic signal with great care. For some musical instruments multichannel anechoic recording was proposed (Rindel et al, 2004).
Besides the generation of signals to be auralized, also their audio-presentation is crucial for a good result.
The playback of an audio signal can be done by using headphones or by usage of loudspeakers in an anechoic room. In case of headphone presentation, an appropriate headphone filter has to be used on listening sample, in order to neutralize its own response. In case of multiple loudspeaker- based listening, crosstalk cancellation needs to be considered.
By realizing all important conditions, auralization can serve as an excellent acoustic presentation tool for an acoustic comfort description.
Auralization also acts as a strong link between room acoustics and virtual reality applications, where technology allows a user to interact with a computer-simulated environment. In the past, virtual reality environments were developed especially for visual experiences, but recent simulations include additional audio information given via speakers or headphones. This approach allows a user to imagine acoustic situation in a place without any knowledge about acoustic numbers.
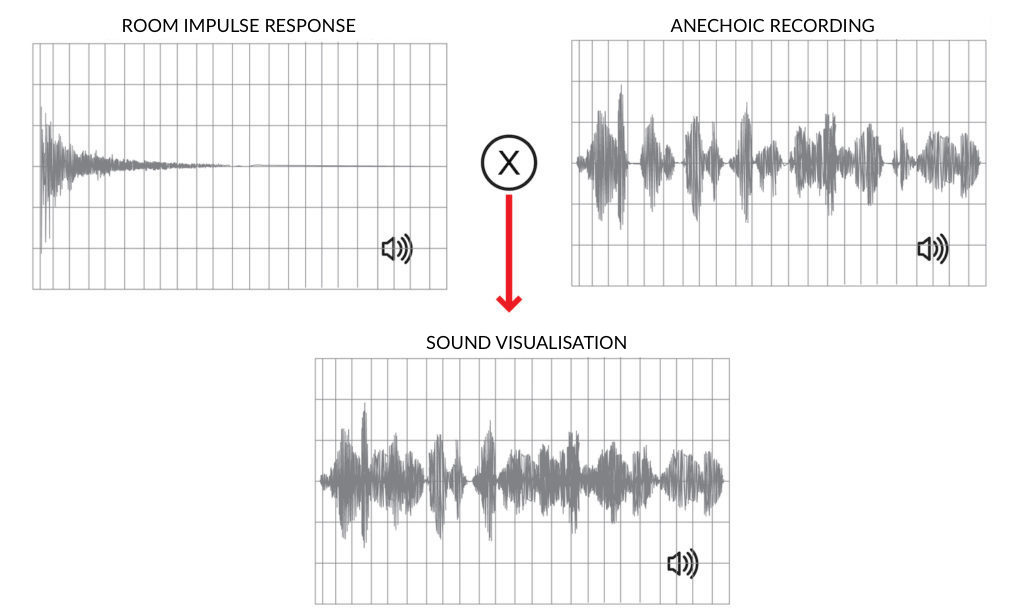 Example of an auralization based on convolution between a room impulse response (measured or simulated) and anechoic recording.
Example of an auralization based on convolution between a room impulse response (measured or simulated) and anechoic recording.
The use of auralization is obvious also in other fields, such as education, hearing research or entertainment.
